PIV in Reacting Flows
2D-2C PIV was applied in the Single Sector Combustor rig (EDS) of the DLR Institute of Propulsion Technology in 2000 using a 2nd generation (cooled) double-shutter PIV camera. The facility was operated at pressures of 3 and 6 bar and inlet temperatures of 570K to 700K. Image magnification is 51,8 µm/pixel (M = 0.13); the laser pulse separation is 4 µs. Further details on this experiment can be found in the book as well as in [1].
Challenges
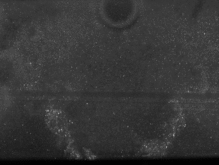
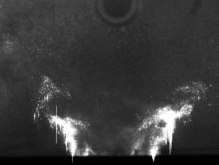
High flame luminosity and unsteady seeding conditions are only two of the challenges in applying PIV in pressurized combustion environments. Also Mie and geometric scattering by fuel droplets of O(10-50 µm) diameter cause sensor saturation.
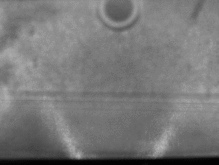

Image conditioning
The following steps were performed to increase image contrast and reduce non-uniformities introduced from the background:
- compute mean intensity image pair from a set of 15 image pairs (more would be better). Note, that the second image is brighter due to flame luminosity being acquired during the integration time of the second frame.
- subtract the mean intensity image pair from the image to be processed.
- if desired, intensity clipping or min-max filtering can further improve image contrast.
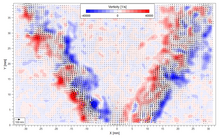
The resulting image pair is shown on the far right.
The image data shown here including background images can be downloaded below.
Downloadable material
-
Raw PIV image pair and matching background images (16 bit TIFF images)
Reference
[1] Willert C., Jarius M. (2002) Planar flow field measurements in atmospheric and pressurized combustion chambers. Exp Fluids 33, 931–939. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00348-002-0515-7
Content provided by C. Willert (DLR), 2024-03-05
